
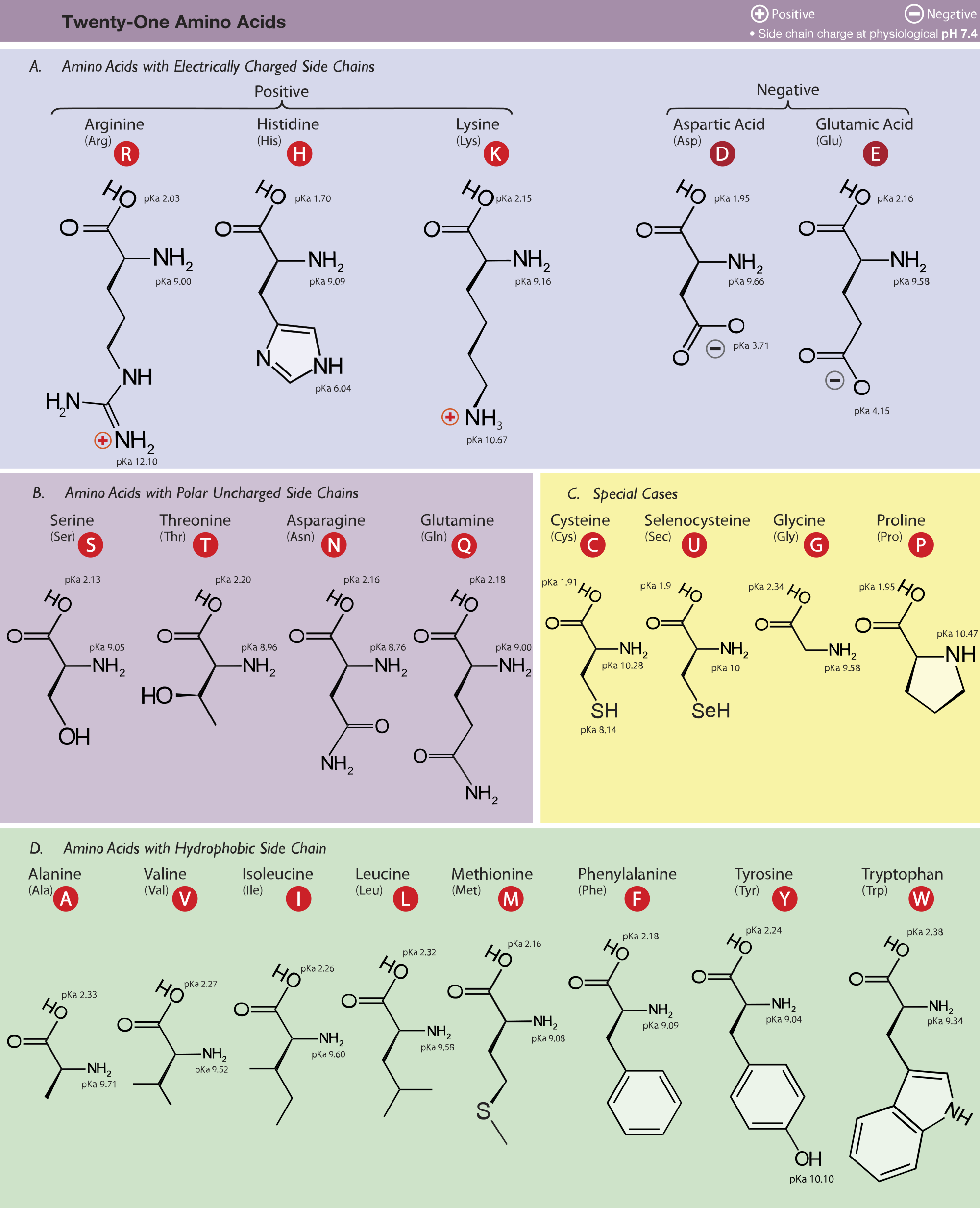
See if you can tell why each amino acid has been sorted in that way. In particular, positively charged amino acids are found in the M2D.

For these amino acids, the deprotonated forms predominate at physiological pH (about 7).Ĭlick on the Protein 1 icon at left to see a chart of all the amino acids, classified according to the chemistry of their side chains. Amino acids that are said to be basic have an extra moiety which will accept electrons (Their side chains contain nitrogen and resemble ammonia, which is a base at neutral pH). Their side chains have carboxylic acid groups whose pKa's are low enough to lose protons, becoming negatively charged in the process.Ĭlick on the structures below to switch between their protonated and deprotonated forms. These are aspartic acid or aspartate (Asp) and glutamic acid or glutamate (Glu). Whereas, cationic charge can be imparted by the presence of the positively charged amino acids arginine and lysine ( Figure 1A), which have a net charge of +1. For these amino acids, the protonated forms predominate at physiological pH (about 7). Their pKa's are high enough that they tend to bind protons, gaining a positive charge in the process.Ĭlick on the structures below to switch between their protonated and deprotonated forms. Administration of the charged amino acids, arginine, and glutamic acid can decrease the seizures of patients suffering from uncontrolled epilepsy. Their side chains contain nitrogen and resemble ammonia, which is a base.
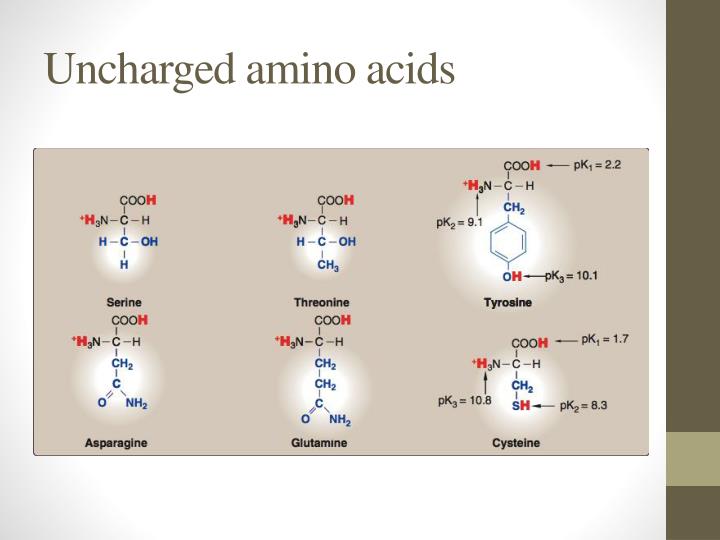
These are arginine (Arg), lysine (Lys), and histidine (His). So for neutral molecules, were looking for amino acids that do not carry a charge, and the charge group is defined by this. Group I amino acids are glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, proline, phenylalanine, methionine, and tryptophan. There are three amino acids that have basic In this problem, we wanted list out the amino acids that exist as witter ions at physiological pH values of around 7.4, but actually exist as neutral molecules.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
